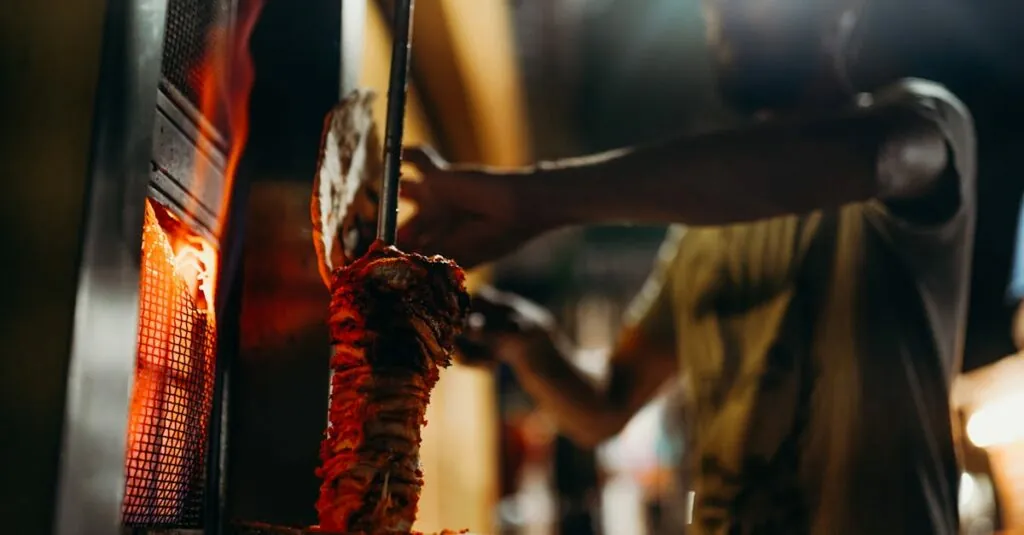Table of Contents
ToggleIndian cooking is a vibrant tapestry of flavors and techniques that can turn any kitchen into a culinary adventure. From the sizzling sounds of tempering spices to the art of slow-cooking curries, these methods aren’t just about making food; they’re about creating an experience that tantalizes the senses. If you’ve ever wondered how a simple pot of rice can transform into a fragrant biryani, you’re in for a treat.
Overview of Indian Cooking Techniques
Indian cooking techniques reflect the vast culinary heritage and geographical diversity of the country. Techniques range from simple methods like boiling to complex ones like fermenting. Each technique plays a crucial role in extracting flavors and enhancing the texture of dishes.
Tempering is pivotal in Indian cuisine. It involves heating oil and adding whole spices, such as mustard seeds and cumin, to release their essential oils. This method enriches the foundation of many dishes, providing depth to curries and dals.
Slow cooking captures the essence of traditional Indian meals. Dishes such as biryani or slow-cooked curries benefit from this method. Slow cooking allows flavors to meld, resulting in a harmonious blend of spices and ingredients.
Grilling offers a smoky flavor, significant in dishes like tandoori chicken. Cooking on skewers or in a clay oven, known as a tandoor, adds distinct characteristics to meat and vegetables. The high heat seals in moisture, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes.
Steaming serves as a health-conscious approach. Techniques such as idli or dhokla showcase dishes prepared without excess oil. This method preserves nutrients and flavors, making it an ideal choice for healthier options.
Frying, particularly deep frying, highlights Indian street food. Pakoras and samosas exemplify this approach, delivering a crispy texture that enhances the overall experience. Frying also lends richness and complexity to flavors.
Fermentation plays a key role in certain staples. Dosa and idli batter rely on fermentation for texture and taste. This process generates beneficial bacteria, contributing to digestion and enhancing the flavor profile of the finished product.
Understanding these techniques reveals the artistry behind Indian cooking, allowing for endless creativity and a rich culinary experience. Each method brings its unique qualities, making Indian cuisine vibrant and diverse.
Importance of Indian Cooking Techniques
Indian cooking techniques possess essential roles in culinary practices across the country. Each method enhances flavors, fosters creativity, and preserves cultural traditions.
Cultural Significance
Cultural identity thrives within Indian cooking techniques. Techniques reflect regional diversity, showcasing unique ingredients and dishes. Cooking methods like tempering and slow cooking represent time-honored practices passed through generations. Grilling and frying are common on festive occasions, linking food to celebrations. Regional dishes embody local history and climate, cultivating pride among communities. Reinforcement of cultural heritage occurs as families gather to share meals prepared using these traditional techniques. Thus, Indian cooking becomes more than mere sustenance; it’s a vital part of cultural expression.
Health Benefits
Health advantages stem from Indian cooking techniques. Steaming offers a method that preserves nutrients in vegetables while minimizing oil use. Using fermentation aids digestion, particularly in staples like dosa and idli. Slow cooking enhances flavor while often using fewer unhealthy fats. Many spices utilized in Indian cuisine, such as turmeric and ginger, present anti-inflammatory properties, promoting overall health. Each technique encourages mindful consumption and promotes a balanced diet. By prioritizing these methods, Indian cooking aligns closely with health-conscious culinary practices.
Traditional Indian Cooking Techniques
Traditional Indian cooking employs various techniques that highlight the intricate flavors and textures unique to its cuisine. These methods reflect regional diversity and cultural heritage.
Tandoor Cooking
Tandoor cooking involves using a clay oven, known as a tandoor. Chefs place marinated meats and breads inside, allowing them to cook at high temperatures. This technique imparts a distinct smoky flavor, often enhancing dishes like naan and kebabs. The intense heat ensures quick cooking while maintaining moisture, resulting in tender meats and perfectly baked breads. Tandoori dishes often feature a blend of spices, showcasing the rich flavor profiles of Indian cuisine.
Dum Cooking
Dum cooking refers to a slow-cooking method typically used for biryanis and other layered dishes. This technique seals the pot tightly to trap steam, allowing ingredients to cook evenly. Aromatic spices infuse flavors deeply throughout the meal. Control over temperature is crucial, as the method relies on low heat for extended periods. Dum cooking achieves tender, flavorful layers, making it a popular choice for festive occasions and family gatherings.
Tempering (Tadka)
Tempering, or tadka, plays a vital role in Indian cooking. This technique involves heating oil and adding whole spices to release their essential oils. The sizzling sound enhances the cooking process, infusing dishes with rich flavors. Typically, cooks add tempered spices to dals, curries, or vegetable dishes at the end of preparation. This method allows for maximum flavor impact, showcasing the art of layering tastes in Indian cuisine.
Regional Variations in Indian Cooking Techniques
Indian cooking techniques vary significantly across regions, reflecting local ingredients, culture, and traditions.
North Indian Techniques
North Indian cooking emphasizes rich flavors and hearty dishes. Tandoor cooking dominates here, allowing marinated meats and naan to develop a smoky taste. Slow cooking also plays a vital role in making dishes like biryani, where spices blend beautifully over time. Tempering, or tadka, enhances dals and curries by releasing the essential oils of spices. Roasting, often seen in vegetables, adds a unique depth to flavors. Cream and ghee enrich dishes, giving a luxurious texture and taste.
South Indian Techniques
South Indian cuisine showcases techniques that elevate simplicity to artistry. Steaming is prevalent for dishes like idli and dhokla, preserving nutrients while creating soft textures. Fermentation is crucial for dosa batter, allowing natural leavening that contributes to the unique flavor profile. The use of coconut, both grated and milk, features prominently in curries and chutneys. Sautéeing with mustard seeds infuses oil with flavor, commonly seen in several vegetarian dishes. Finally, dry roasting spices before grinding intensifies their aroma and taste.
East Indian Techniques
East Indian cooking highlights fresh ingredients and subtle flavors. Fish is often prepared using steaming, which maintains its delicate texture and taste. The region favors preparing pithas, where rice flour wraps around fillings and is steamed, offering a unique culinary experience. Sautéing with panch phoron, a unique spice blend, enhances dishes while providing a trademark profile. Braising is common for meats and vegetables, allowing flavors to meld and intensifying aromas. Lastly, the use of sweets, like rasgulla, showcases the region’s penchant for balancing flavors and textures.
West Indian Techniques
West Indian cuisine reflects a vibrant palette of techniques tied to the region’s climate and history. Sundrying is widely practiced to preserve ingredients like fish and spices, adding intensity to flavors. The region often employs tempering with a variety of spices in hot oil to create aromatic masalas, lending richness to dishes. Grilling, particularly in coastal areas, provides a smoky essence to seafood and meats. Curry preparations frequently involve dry roasting spices before grinding to unleash enhanced aromas. Lastly, layering flavors through slow cooking creates depth in dishes like dhokla and vindaloo.
Modern Adaptations of Indian Cooking Techniques
Modern adaptations of Indian cooking techniques enhance the traditional methods with innovative approaches. Chefs frequently use pressure cookers to cut down on cooking time while maintaining flavor. The popularity of air fryers showcases a growing preference for healthier cooking, allowing for crisp results with less oil.
Fusion cuisine increasingly blends Indian spices with global ingredients, creating unique dishes. For instance, tandoori chicken tacos combine the rich flavor of marinated meats with a familiar format, appealing to diverse palates. Additionally, plant-based cooking has gained traction, leading to the use of traditional techniques such as tempering with alternatives to dairy or meat, making dishes more inclusive.
Technology plays a significant role in modern adaptations. Smart kitchen appliances, such as induction cooktops, offer precise temperature control, which improves the consistency of slow-cooked curries. Online cooking classes introduce enthusiasts to regional methods, providing greater access to authentic Indian cuisine.
Presentation also shifts with modern influences. Plating techniques transform traditional dishes into visually appealing arrangements, enhancing the dining experience. Ingredients are often sourced locally to emphasize freshness, demonstrating commitment to sustainability alongside tradition.
Social media has revolutionized how Indian cuisine is perceived globally. Videos and posts showcasing quick recipes or cooking tips reach a wide audience, inspiring more to explore Indian cooking. Community engagement via food blogs assists in sharing these adaptations and encourages culinary experimentation.
Overall, the fusion of modern techniques and traditional methods continues to evolve, creating an exciting landscape for Indian cooking. Each adaptation respects the roots of Indian cuisine while embracing contemporary tastes and preferences.
Indian cooking techniques embody a rich tapestry of tradition and innovation. They not only enhance the flavors and textures of dishes but also connect generations through shared culinary practices. As modern adaptations emerge they breathe new life into age-old methods while preserving the essence of Indian cuisine.
The fusion of traditional techniques with contemporary approaches showcases the adaptability of Indian cooking. This evolution invites everyone to explore diverse flavors and celebrate the cultural significance behind each dish. Whether it’s through the artistry of tempering spices or the health benefits of steaming, Indian cooking remains a vibrant expression of heritage and creativity.